Coronavirus: How to respect obligations without panicking
LAST MINUTE NEWS
Every day, coronavirus disease “nCoV-2019” outbreak is getting bigger, the national territory as a whole is now affected, with several so-called “cluster” areas.
How to respect its obligations without giving in to panic, to adapt its activity and organization, to limit the negative consequences for the company, to deal with suspected or even proven cases among its staff, what would be the impact of the transition to “stage 3” presented as imminent, the questions that employers must answer on a daily basis are numerous and the answers are constantly changing.
DUTY OUTLINE
The employer has a safety obligation towards the employees and must take all measures to ensure their safety and protect their physical and mental health.
Article L. 4121-1 of the Labor Code: « The employer shall take the necessary measures to ensure the safety and protect the physical and mental health of workers.
These measures include:
- Actions to prevent occupational risks, including those mentioned in Article L. 4161-1 ;
- Information and training actions ;
- The setting up of an organization and appropriate means.
The employer shall ensure that these measures are adapted to take into account changing circumstances and aim at improving existing situations. »
The employer can be held liable in the event of a suspected or realized risk, unless he is able to demonstrate that the necessary preventive measures have been taken to avoid it.
For their part, employees must comply with their employer’s guidelines and respect the health requirements given to them.
Article L. 4122-1 of the Labor Code: « In accordance with the instructions given to him/her by the employer, it is the duty of each employee to take care, in accordance with his/her training and according to his/her possibilities, of his/her own health and safety and that of the other employees concerned by his/her acts or omissions at work. »
WHAT ARE THE RECOMMENDATIONS TO FOLLOW?
[/su_spoiler]Even in absence of any suspicious cases in the workforce, it is recommended to issue a communication to all employees detailing in particular:
- A reminder that transmission of the virus occurs through “close contact” with an contaminated person, i.e. in the same area, direct contact within one meter when coughing, sneezing or talking for more than 15 minutes in the absence of protective measures.
- Protective hygiene measures to be adopted in all circumstances : – more details on the WHO website: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public
- The number of the information contact platform launched by the French state for any questions linked to the virus with the exception of medical questions: 0800 130 000
- Dedicated websites:
– French government information website (available only in French): https://www.gouvernement.fr/infocoronavirus
– Travel advice from the Ministry of Europe and Foreign Affairs (available only in French) : https://www.diplomatie.gouv.fr/fr/conseils-aux-voyageurs/conseils-par-pays-destination/
– Q&A on WHO website: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses - The procedure to be followed internally for employees according to their specific situation :
– employees identified by the regional health agency as high-risk contact cases and therefore placed in isolation
– employees returning from high-risk areas (abroad or in France) and/or identify as contact cases (but not high-risk)
– employees whose child is subject to a period of isolation or is in an educational institution closed - A reminder of the specific measures put in place so that employees prevented from working because of Covid-19 without being contaminated (employees who have to be placed in quarantine or whose children cannot go to school) can receive daily indemnities from the social security system (without waiting periods).
- Instructions for business trips (whether in high-risk areas or whatever the destination): restriction, freezing, express prior authorization, etc. or even recommendations for employees’ private travel (the Ministry of Europe and Foreign Affairs now recommends postponing non-essential travel abroad, particularly outside the European Union, to limit the spread of the virus).
- As the case may be: the company makes available hydroalcoholic gel and/or masks for the employees in the workplace(s).
Whether it is the situation of employees returning from high-risk areas, residing in or returning from an area of active circulation of the virus in France, that of employees with children placed in a quarantine or whose school is closed, or that of employees who may have been in contact with infected persons (contact cases whether or not at high risk), there are many individual situations which will need to be dealt with.
To this end, it is advisable to appoint one (or several) point(s) of contact within the company, for both the employees and the authorities.
In addition, the point of contact may be responsible for monitoring / assessing the situation in the company, by identifying :
- employees returning from high-risk areas,
- employees who have been in contact with suspected or infected persons,
- employees posted / expatriated in high-risk areas,
- the measures taken for each situation (information, training, teleworking, contact with medical services, hospitalization, isolation, etc.).
In order to ensure this follow-up, it could be envisaged to distribute a survey to each of the employees. This survey would allow making the employees more responsible towards the community as well as demonstrating that the employer has fulfilled its safety duties.
When contacts are long and close, employers must adopt specific measures that complement the protective measures recommended by the public health authorities (greeting without shaking hands, avoiding hugging, washing hands very regularly, coughing or sneezing into the elbow, using single-use tissues) such as, for example: the installation of a courtesy zone of at least one metre, regular cleaning of surfaces with an appropriate product, the supply of hydroalcoholic gel and single-use tissues in sufficient quantities, etc.
In addition to cases of information and/or consultation of representative bodies on given subjects (such as updating the risk evaluation document, implementation of the partial activity, etc.), it seems advisable to regularly inform employee representatives of the situation in the company, of all the measures implemented and their evolution.
In addition, the Social and Economic Committee (“CSE”) may be convened at the reasoned request of two of its members on matters relating to health, safety or working conditions.
The Labor Ministry considers that the updating of the single risk evaluation document provided for in Article R. 4121-2 of the Labor Code is required in view of the current epidemic due to the COVID-19 virus and that it must provide for adequate prevention and protection measures to reduce the risks of contagion in the workplace or during work as much as possible.
This updating requires the intervention of the staff representative bodies (CSE) and the occupational health service.
In the event that external companies operate on the workplace, it will also be necessary to update the applicable prevention plans in accordance with the provisions of Article R. 4513-4 of the French Labor Code.
- Inform without delay the occupational health authorities and the regional health agency to which the establishment is subject.
- Clean the work areas that the employee concerned has been able to access.
- Encourage teleworking wherever possible. Otherwise, reorganize the workplace(s) concerned in order to limit contacts as much as possible.
If teleworking is not possible, make sure that the employees concerned:
- scrupulously respect the adapted gestures;
- avoid places with fragile people, non-essential meetings (conferences, meetings, seminars, etc.), places that could lead to close contacts (canteen, lifts, etc.).
In case of suspicions, with quarantine / isolation, or even proven cases within the company, the first reflex of the employer should be to alert the occupational doctor and the regional health agency on which it depends.
The employer should also ask the employees concerned to list all the people with whom he/she has been in contact both within the company and with the company’s service providers, customers, etc., and determine the communication and actions to be implemented with regard to these people in relation to the health authorities.
In the case of a quarantine placement, it will be necessary to study with the employee the possible options (mainly teleworking or not).
With regard to workplace areas, in the event of proven contamination, the Government recommends the following measures, as the coronavirus can probably survive for several hours on dry surfaces:
- cleaning with an appropriate product of all areas to which the employee concerned may have had access;
- equipping the persons in charge of cleaning with a single-use gown and household gloves (it is not necessary to wear a respiratory protection mask due to the absence of aerosolization by floors and surfaces);
- maintenance of floors by favoring a wet wash-disinfection strategy so that:
– floors and surfaces are cleaned with a single-use wash strip impregnated with a detergent product,
– the floors and surfaces are then rinsed with water from the drinking water system with another single-use wash strip,
– a sufficient drying time of these floors and surfaces,
– floors and surfaces must be disinfected with bleach diluted with a different single-use wash strip than the previous two.
If an employee refuses to comply with an isolation placement recommended by the regional labor authority or teleworking, for instance, it will be possible to implement a disciplinary procedure against him/her and, if necessary, a temporary disciplinary lay-off.
Si un salarié refuse de respecter un placement à l’isolement préconisé par l’ARS ou le télétravail par exemple, il sera possible de mettre en œuvre une procédure disciplinaire à son égard avec, le cas échéant, une mise à pied à titre conservatoire.
TO DEAL WITH A DECREASE IN ACTIVITY: POSTPONING THE PAYMENT OF CONTRIBUTIONS
If an employee refuses to comply with an isolation placement recommended by the ARS or teleworking, for example, it will be possible to implement disciplinary proceedings against him or her, including, if necessary, a protective layoff.
The government announced that companies could request the deferral of their social security and tax charges as of the beginning of March.
The URSSAF specifies on its website that this request can be made either online from each company’s space by sending a message via the heading “A declarative formality”> “Declare an exceptional situation” or by telephone at 3957.
For its part, the Treasury refers to the following email address: covid. dge@finances.gouv.fr
Finally, on March 12, 2020, Bruno Le Maire declared “We are going to propose this postponement to them. It is not up to them to ask for it, it is the social and fiscal administration that will propose to companies the deferral of their social charges and tax charges, he said. If at the end of the day companies can’t pay, we’ll give them tax breaks. »
TO DEAL WITH A DECREASE IN ACTIVITY: THE PARTIAL ACTIVITY SYSTEM
The Labor Ministry has confirmed the possibility of using the partial activity system in the context of a drop in activity due to the Covid-19 epidemic (Questions and Answers for companies and employees of the Labor Ministry updated on March 9, 2020).
This system aims at allowing an employer to reduce working hours temporarily, or even to suspend the activity of employees, when the company is faced with economic difficulties compelling it to temporarily reduce its activity due to exceptional circumstances or economic conjecture (Article R.5122-1 of the Labor Code).
The implementation of this system leads to a reduction in the working hours of certain employees below the legal or conventional weekly working hours required :
- prior consultation of the Social and Economic Committee on the grounds for the use of this mechanism, the professional categories and activities concerned, the level and procedures for implementing suspensions of activity or reductions in working hours (Article L.2312-8 of the Labor Code).
- obtaining a partial activity authorization: the request must be motivated and thus specify (i) the reasons justifying the use of the partial activity, (ii) the foreseeable period of partial activity, and (iii) the number of employees concerned. The CSE’s position shall also be transmitted to the administration.
Requests shall be examined within 15 days of the date of receipt, and failure to take a decision within that period shall be deemed to constitute implicit approval of the request. The CSE must be informed of the administration’s decision (Article R.5122-4 of the Labor Code).
Requests must be submitted on the dedicated portal : https://activitepartielle.emploi.gouv.fr/aparts/ before the actual placement of employees in partial activity.
However, if it is not possible to anticipate applications for partial activity, it is foreseen that employers may submit their application for partial activity within a reasonable period of time after the start of the period applied for.
- the individual information of the employees as well as, if necessary, the communication of the changes made to the collective working hours to the labor inspector (article D.3171-17 of the labor code).
For all non-working hours up to the legal weekly limit of 35 hours, the employee benefits from an indemnity paid by the employer, corresponding to a percentage of his/her gross remuneration (70% of the gross hourly remuneration).
To supplement the payment of this indemnity, the employer shall receive, for each hour off work, an allowance jointly financed by the State and the body managing the unemployment insurance system (Unédic) at a rate of:
- 7,74 euros per hour off work for companies with less than 250 employees
- 7,23 euros per hour off work for companies with more than 250 employees
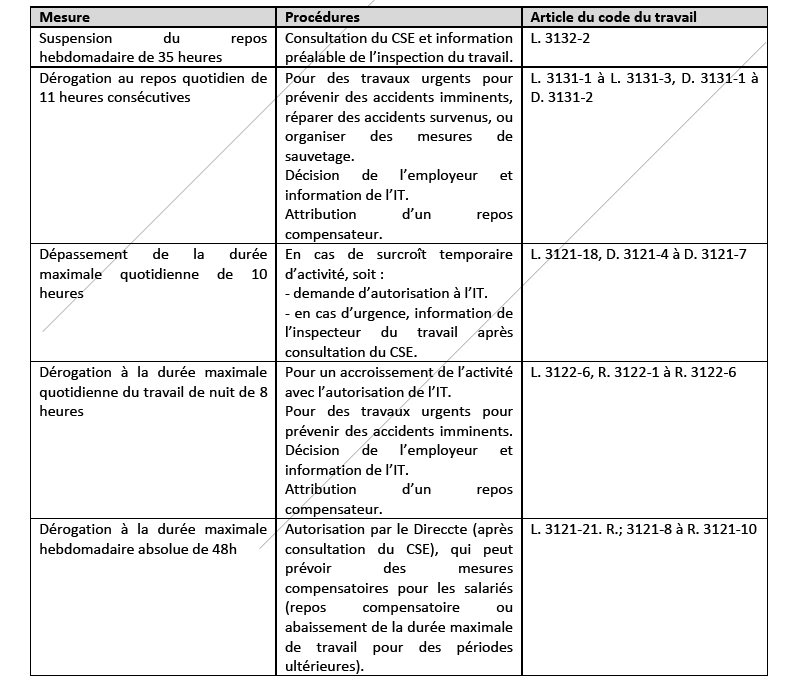
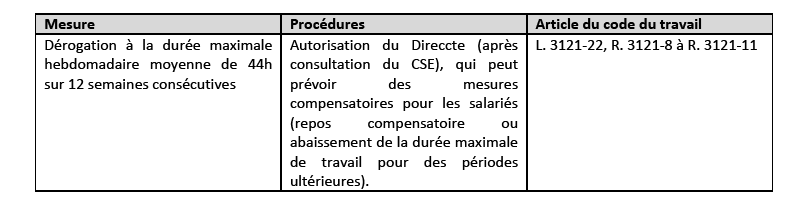
In its questions/answers for enterprises and employees updated on 9 March 2020, the Labor Ministry has detailed the provisions of the Labor Code allowing for derogations from the maximum working hours and rest periods as follows :
These measures may be applied in emergency situations for limited periods of time after informing the labor authority.
Even if the agreement of the employees is still to be favored, teleworking can be implemented unilaterally when the layout of the workplace is made necessary to allow the continuity of the company’s activity and to guarantee the protection of the employees.
Article L. 1222-11 of the Labor Code refers to the risk of epidemic as a possible justification for teleworking without the employee’s consent.
The implementation of teleworking in this framework does not require any particular formalism. However, the CSE must be consulted in the event of a major change in the organization of work (Article L. 2312-8 of the Labor Code).
More and more companies are requiring their service providers, suppliers, customers, etc. able to visit their sites to provide certificates of non-contamination for their employees and/or to transmit information on employees suspected of being contaminated and/or contaminated employees.
This is medical data and therefore particularly sensitive.
On the basis of a reminder of the applicable rules issued by the CNIL (https://www.cnil.fr/fr/coronavirus-covid-19-les-rappels-de-la-cnil-sur-la-collecte-de-donnees-personnelles), the communication of personal data on employees to third parties does not seem possible or even desirable.
Should we buy masks?
Apart from the supply difficulties, this does not seem necessary as masks are only recommended for people who are ill and therefore no longer present in the company.
Can we monitor the temperature of employees?
This is an extremely intrusive measure that can only be justified by very specific circumstances (employees in prolonged and close contact with fragile people, for example) and cannot be systematized for all employees given the current situation.
Should teleworking be systematized?
At this stage, this would be a preventive measure. This does not seem necessary, but it may make it possible, in particular, to test the IT infrastructure and the way in which the teams operate in this configuration in order to make the necessary adjustments if and when teleworking is required. Some companies use it on a more or less large scale and encourage their employees to take their computer equipment with them each evening to be able to telework if necessary.
Should we cancel meetings, seminars?
In the present circumstances, a general ban on any physical meeting or seminar does not seem necessary and a case-by-case analysis should be favored, making sure that recommended gestures are respected for those that will be maintained and, to the extent possible, arranging the areas in such a way as to leave a distance of at least one meter between each participant.
What about employees’ right of withdrawal?
Under Articles L. 4131-1 and following of the Labor Code, an employee may withdraw from a work situation in which there are reasonable grounds for believing that it presents a serious and imminent danger to his or her life or health. The employee must alert the employer of this situation. This is an individual and subjective right.
The government’s position is that unless employers take no action, the exercise of the right to opt-out by employees in the current context would not be justified. However, this is a matter for the discretion of the courts.
Our employment law team is at your disposal for any questions you may have regarding the above.



Legal Alert – Russian Counter-Measures
Recently the Russian competent authorities have adopted new counter measures. In particular, such measures concern trade regulation, conduct of business, as well as the activities of the Government Commission and others. To find out more, download the Newsletter or click here. For more information on sanctions and Russian counter measures, please refer to our previous “Legal Alerts“.
Moscow Desk
Sanctions Against Russia. Recent Developments
On 23 February 2024 European Union and the United States introduced a new round of sanctions targeting Russia. The 13th package of European sanctions provides for new individual sanctions, sectoral sanctions, export restrictions. Additionally, EU added the United Kingdom to the list of partner countries for the iron and steel import restrictions. American sanctions include […]
Moscow Desk
Newsflash – Corporate – Venture Capital – French government announcements to support Innovative Startup Companies (JEI)
For the occasion of the French Tech’s 10th anniversary, new measures stemming from the report of Parliament Member Paul Midy (for which Jeantet had been consulted) have been announced. These measures, which aim at supporting the French startup ecosystem, should be included in the next Finance Act for 2024. ► Doubling of companies eligible to […]
| CORPORATE – M&A – PRIVATE EQUITY
Russian Counter Measures. Recent Developments
On 23 August, the Russian Ministry of Finance partially lifted a ban for the payment of dividends to foreign shareholders in case such shareholders have invested in the Russian economy. On 8 August, the Russian President suspended certain provisions of double tax treaties. Suspended provisions include tax regime for dividends, real estate, business profit, etc […]
Moscow Desk
Sanctions Against Russia. Recent Developments
On 23 June 2023, the EU introduced 11th package of sanctions. It primarily focuses on measures that would prevent circumvention of sanctions. It also includes new import and export restrictions and individual designations. Switzerland has joined European Union in sanctions targeting entities and individuals and may join other sanctions within the 11th package in August. […]
Moscow Desk
Newsletter – Tax law
Read the Jeantet Newsletter dedicated to Tax Law, covering issues related to : Transactional taxation Group taxation International Taxation Taxation of LBO transactions Non-profit organizations For more information, please download the Newsletter.
Paris | TAX
Russian Counter Measures
On 25 April 2023 Russian President issued a decree establishing cases authorizing him to introduce the regime of external management of certain assets owned by foreign residents. Namely, under the decree, the President may establish the regime of external management, if Russia, or its entities and individuals become deprived or risk of being deprived of […]
Moscow Desk
Russian counter measures and measures aimed at business support. Recent developments
Special regime for transactions involving securities On 3 March 2023 Russian President issued Decree No. 138 establishing additional measures involving securities. Namely, the new Decree establishes a specific procedure for transactions / operations involving: shares of Russian joint-stock companies, sovereign bonds, bonds of a Russian issuer, held in collective safe custody of a Russian depository, […]
Moscow Desk
Sanctions against Russia. Recent developments (2 march 2023 update)
By the end of February, the EU, US and UK announced new rounds of sanctions, all of them including restrictions targeting prominent Russian financial institutions The EU package includes individual listings of Russian entities and individuals and additional exports restrictions. The US sanctions provide for sectoral sanctions targeting Russian mining and metals sector, as well […]
Moscow Desk
Russian counter measures. Recent developments ( 12 january 2023 update)
Governmental Commission on Foreign Investments revised rules on the sale of assets and the payment of dividends On 30 December 2022, Russian Governmental Subcommission of the Commission of the Ministry of Finance on Foreign Investments (the – Commission) published revised rules and criteria for authorization of the sale of assets in Russian companies involving persons […]
Moscow Desk
Sanctions against Russia. Recent Developments (21 December 2022 update)
This December, the EU introduced a series of restrictive measures targeting Russia. Council of the EU approved the ninth package of sanctions. Additionally, the European Commission proposed framework that would amend the Lisbon Treaty and harmonize criminalization of violation of sanctions at the level of the Union. Finally, the EU introduced a price cap for […]
Moscow Desk
Russian counter measures. Recent developments (21 December 2022 update)
Russia has adopted a series of new measures. Namely, the President introduced new restrictions concerning certain transactions involving credit organizations and joint-stock companies that are not credit organizations. The Russian Central Bank issued decision expanding the scope of application of type C accounts. Moreover, the Ministry of Finance issued clarifications on the scope of transactions […]
Moscow Desk